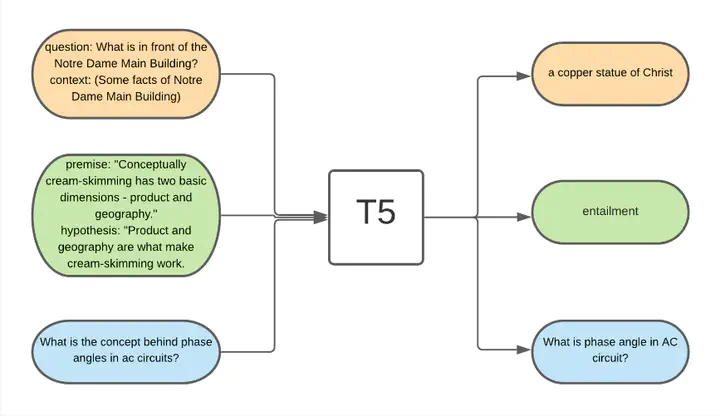
In the domain of Natural Language Processing, it is unheard of for models to be trained on multiple
tasks sequentially. This is because after the first task, there is
a significant dip in performance on the first task while training
for the second task. This is known as catastrophic forgetting.
Continual learning aims to combat this problem by retaining
knowledge of previous tasks while being able to adapt to any
new task. We utilize a loss based method called Elastic Weights Consolidation and apply it on the T5 transformer to enable it to adapt to almost any NLP task while
being fast and memory efficient.
Check out the slides, paper and the code on GitHub for more details!